DNA origins test
Discover all about your ancestry! At tellmeGen, we have a comprehensive ancestry section where you can learn about your paternal and maternal haplogroups, the percentage of Neanderthal DNA in your genetic makeup, and even how your heritage is distributed across different populations and ethnicities with a high degree of accuracy.

What do we do in our DNA test to know your origins?
In our DNA Origins test, we analyze the genetic variants that appear in the autosomal region of your DNA, commonly known as SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms), to determine your ancestry. SNPs are a type of genetic marker that is very useful for determining ancestry because each population has unique genetic variants.
Phase 1: Quality control of the genetic material
After purchasing the ancestry service kit and collecting the necessary fraction of your genetic material, it undergoes strict quality controls. Only the genetic markers that meet the requirements for the analysis are kept, which helps us minimize possible deviations in our estimations and generate highly accurate results.
Phase 2: Study your DNA to determine your ethnicity
After collecting a fraction of your genetic material and subjecting it to strict quality controls, we compare it to a vast database containing thousands of reference individuals from 53 ethnic groups across 7 geographic regions: Europe (27), Africa (6), West Asia (4), South and Central Asia (6), East Asia (6), Oceania (2), and the Americas (2). With our latest update to the DNA ethnicity test, we can provide even more detailed ancestry information by breaking down the reference populations into more specific regions.
The creation of reliable reference populations is a crucial aspect of our ancestry estimation process. Accurate reference populations enable us to determine the genetic origins of each of our users with greater precision. To achieve this, our bioinformatics experts have analyzed genetic information from individuals from various geographical regions in our database, using powerful statistical and bioinformatics tools, as well as quality control measures. Through this methodology, our algorithm can accurately distinguish between the populations that contribute to the genetics of each of our users, minimizing the errors derived from statistical inference. This makes tellmeGen's DNA testing for ethnicity one of the most comprehensive and dependable options available.
Phase 3: ancestry service report
After completing the ancestry estimation process, you will receive a comprehensive ancestry report that includes the percentage breakdown of your unique genetic composition in different ethnic groups organized by geographical location. These values, based on your DNA, reflect the ethnic origin of your ancestors.
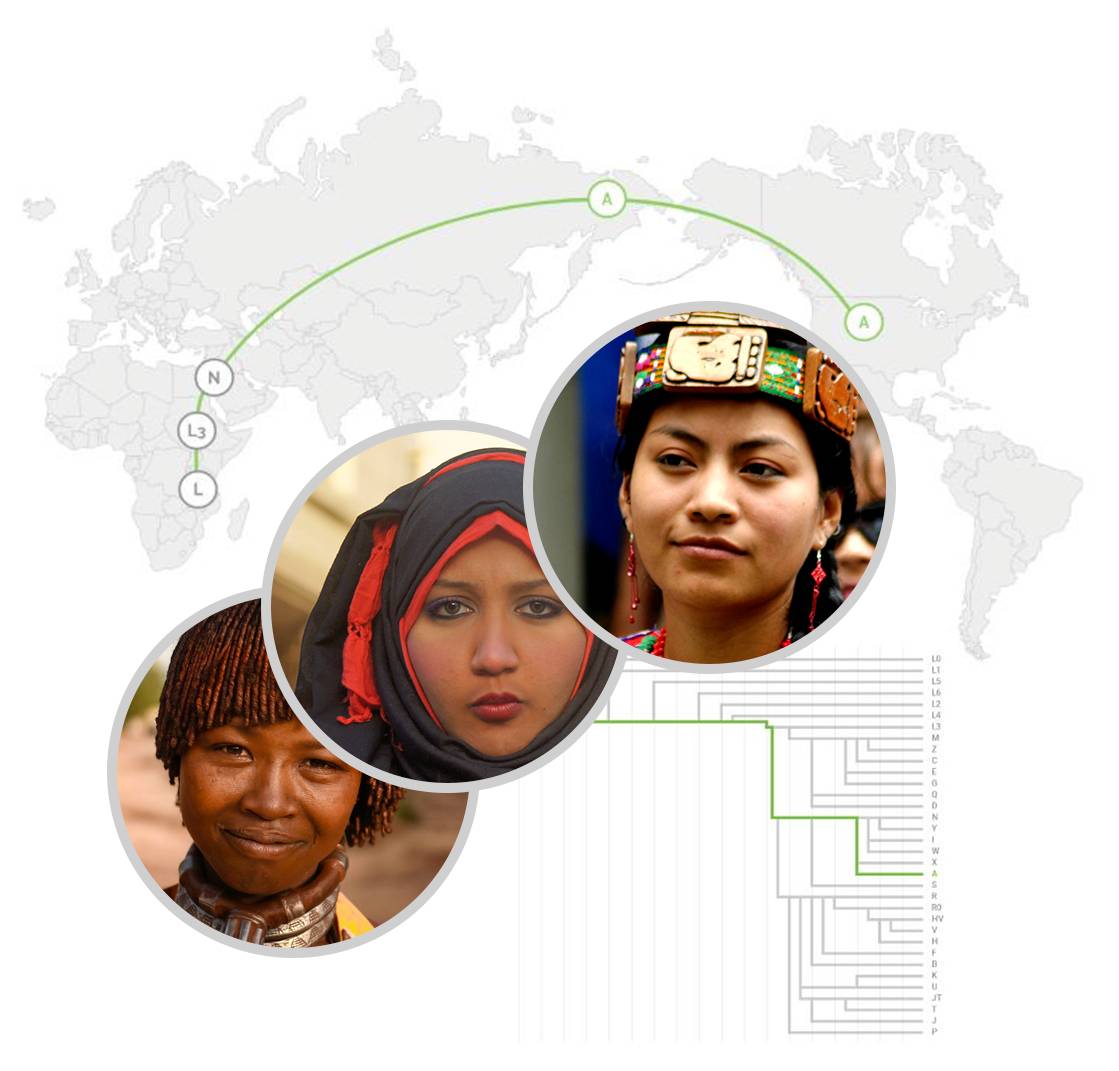


Discover your maternal haplogroup
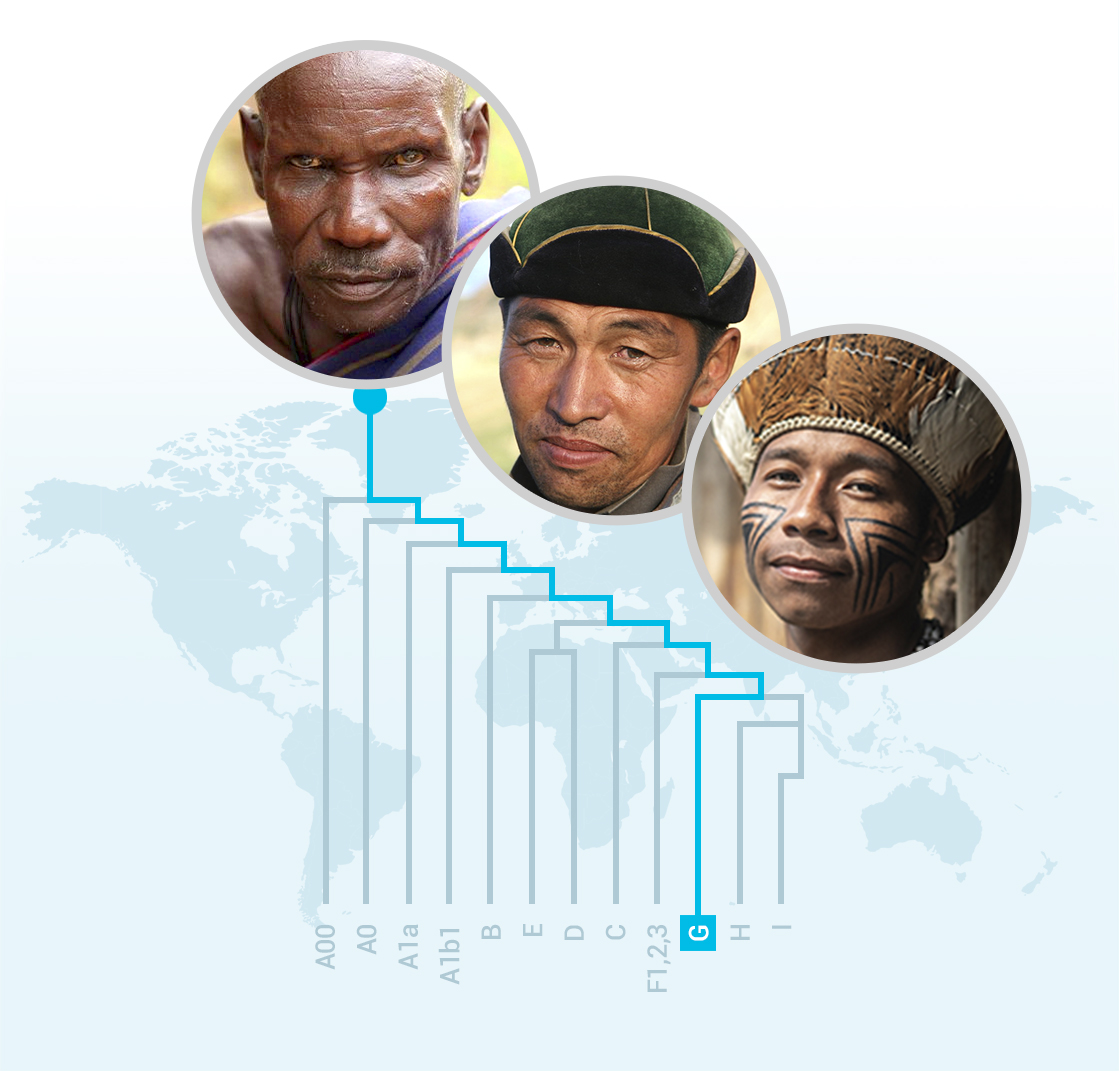
Trace and discover your paternal haplogroup
It is important to note that the paternal haplogroup can only be obtained from males. If you are born female, a sample from your father or a male sibling is necessary, as this information is only extracted from the Y chromosome. However, this is independent of the other results related to your ancestry, which are obtained by analysing your genetic information from both your father and your mother.


Know your Neanderthal DNA percentage
Did you know that humans today share up to 4% of our DNA with the Neanderthal species?
Neanderthals emerged approximately 230,000 years ago in Europe, the Near East, the Middle East and Central Asia.
This species, which lived at the same time as Homo sapiens, had a stocky build and weighed around 70 kg. They had short limbs, a wide pelvis, and a strong skeletal structure that indicated a highly muscular body.
Although their diet was long considered to be meat-based, more recent studies show that it was very diverse and adapted to their environment.
Neanderthals were also knowledgeable about fire, using it for cooking, as well as for making rudimentary medicines.
The extinction of the Neanderthals occurred around 28,000 years ago. According to most studies, the expansion of our species, Homo sapiens, from Africa was the main cause of their disappearance, despite the interbreeding that occurred between the two species.
Would you like to know more? Find out how you are related to this species thanks to the Neanderthal DNA test.
Reference populations in our ancestry genetic test
To ensure that our genetic ancestry testing is one of the most complete on the market, tellmeGen's database includes thousands of individuals belonging to 53 ethnic groups distributed across 7 geographic areas: Europe (27), Africa (6), West Asia (4), South and Central Asia (6), East Asia (6), Oceania (2), and the Americas (2).
Europe

The Ashkenazi Jewish population is a group that currently consists of approximately 10 million people. Their origin dates back some 2000 years, when their ancestors moved from Western Asia to Central Europe. Their history is marked by the persecution, genocides and Holocaust that took place during World War II. This historical event caused Jews to emigrate all over the world. At present, the most representative groups of Ashkenazis are distributed among the United States, Israel and the former Soviet Union. Within this community, consanguineous marriages are a common practice, so it has become a very characteristic and homogeneous population from the genetic point of view.

Sardinia is an island located in the center of the Mediterranean Sea, bordering Corsica to the north, the Italian peninsula to the east, Tunisia to the south and the Balearic Islands to the west. This island has approximately 1.5 million inhabitants, and its history is quite ancient and rich. The first settlements in the territory occurred more than 10,000 years ago, and came from the Italian peninsula, the Iberian peninsula and Africa. Since that time, the Sardinians have not undergone major migrations. This fact, together with the geographical situation of the territory, has made the genetics of Sardinia very characteristic and different from the rest of the populations of its geographical environment.
America

item.ancestry.superpoblation.overview.AMR_AMZ

Distributed throughout the northern part of the American continent is the population of the native Pima people. It is an ethnic group that currently has a few hundred inhabitants of purely Pima genetics. The first region inhabited by this people was western Canada, and from there it expanded to occupy a large part of the continent. At the genetic level, it has been verified that the Pima descend from the first inhabitants of the American continent, who came from East Asia.
Oceania

Melanesians are the indigenous inhabitants of Melanesia, a region of Oceania that extends throughout the western part of New Guinea. Several scientific studies indicate that the first inhabitants of the region arrived during the migration of Africans to the Asian continent. Years later, there were several waves of settlement of Austronesian peoples in the territory, giving rise to numerous complex genetic mixtures.
Africa

With a population of approximately 47 million inhabitants, Kenya and Uganda are the two African countries located in the easternmost part of the continent. Different ethnic groups have been settled in this region for several centuries, with the Luhya and Luo peoples being the most representative. These groups initially settled in the east and west of Uganda, although during the second half of the 15th century they migrated to western Kenya. For this reason, these two regions share a high degree of genetic similarity.

The Maghreb is a region located in North Africa whose genetics is mainly represented in the countries of Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, Western Sahara and Tunisia. It has a population of more than 100 million inhabitants. The first settlers of the Maghreb were the Imazighen, better known as Berbers. Since then, the Maghreb territory has received several migratory waves such as the arrival of the Andalusians, the Ottoman Empire or the French colonization. For this reason, the Maghrebi population shares a large part of its genetics with some southern European countries.

With a population of approximately 20 million inhabitants, The Gambia and Senegal are the two West African countries located furthest west on the continent. The genetics of The Gambia and Senegal have been strongly marked by historical episodes of human and commercial mobility, being the epicenter of African slavery between the 16th and 18th centuries. Nowadays it is a region where different ethnic groups have settled down, being the Mandinga the most representative: more than 30% of the inhabitants of Gambia and Senegal belong to this group.

Located in West Africa and with approximately 230 million inhabitants, are Nigeria and Ghana. The history of this African region has been marked by constant European expeditions to the Gold Coast, a fact that is reflected in its genetics. As a result of this genetic diversity, more than 250 ethnic groups have been identified in the region, the most important being the Esan people and the Yoruba people.

With a total of 8 million inhabitants, Sierra Leone and Liberia are located in West Africa. The origin of both countries is closely related, as it dates back to the struggle that took place in the 18th century against slavery on both sides of the Atlantic. Numerous populations have now settled throughout the territory, although the Mende are the most characteristic ethnic group, representing 30% of the total population.
Central and South Asia

Bangladesh and Northeast India are situated in an exceptional geographical position, which has shaped the current genetic mosaic of the region. The first populations to settle in the area were Austroasiatics, Tibeto-Burmans, Dravidians, and Indo-Europeans. For this reason, the inhabitants of Bangladesh and Northeast India share genetic markers with East Asian populations.

Central Asia is a territory with a large number of ethnic groups, distributed mainly in five countries: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan. The origin of this population dates back to the Indo-Iranian and Turkic expansions that took place centuries ago. As a result, today's Central Asians share a high degree of genetic similarity with the peoples of Western Asia.

The Gujarati people are an ethnic group of approximately 60 million individuals. They originate from the state of Gujarat, located in the northwest of the Indian subcontinent. Given its complex history, it is a people with a high genetic diversity. For several centuries, the state of Gujarat has been a meeting point for important migratory flows, mainly between the coasts of the Arabian Sea, a region with which it shares a certain degree of genetic similarity.

Southern India and Sri Lanka is a region of more than 230 million people, mainly spread over the states of Andhra Pradesh, Tamil, Nadu, Karnataka and Kerala, as well as the island of Sri Lanka. Most of the inhabitants of this region belong to the Telugu people, the majority ethnic group in the territory. The Telugus, like some other South Asians, are descended from a mixture of pre-Dravidian, Dravidian and Indo-Aryan tribes that first settled in the territory more than 70,000 years ago.
East Asia

The Japanese are a group native to the archipelago of Japan, located in East Asia. The oldest archaeological evidence from this region corresponds to groups of hunter-gatherers dating back more than 39,000 years, when there was still a land connection between the archipelago and the Asian continent. Geographically, several ethnic groups can be distinguished in the territory, including the Yamatos, the Ainus and the Ryukyuan. However, the Yamatos are the most numerous people and the term Japanese generally refers directly to this group.

Koreans are one of the largest groups in East Asia. The population numbers approximately 80 million individuals, distributed in both northern and southern Korea. It is thought that the first settlers of this group descended from the ancient peoples of Manchuria, Mongolia and southern Siberia, who settled in northern Korea during the Bronze Age. Today, it is one of the most genetically homogeneous populations in the world.
Western Asia

The name Bedouin is attributed to the nomadic Arab population inhabiting the deserts of the Near East, the Arabian Peninsula and North Africa. It is estimated that this ethnic group is made up of more than 25 million individuals, settled mainly in Sudan, Algeria, Saudi Arabia and Iraq. Its origin dates back to 7th century Arabia and its rapid expansion throughout Western Asia. Today, the Bedouin people are a genetically heterogeneous people. Depending on the places to which they migrated, subgroups of nomads have formed that may share high genetic similarities with the Turks, Kurds or Arabs.

The Druze are a religious and cultural community originating in the Levant, with a majority presence in Lebanon, Syria, and Israel, and smaller communities in Jordan. Emerging in the 11th century from Ismaili Islam, they have developed a unique faith incorporating Neoplatonic, Gnostic, Christian, and other systems of thought. Traditionally settled in mountainous regions, they have preserved a cohesive identity, with strong community ties and a social structure based on solidarity, education, and respect for ancestral wisdom. Although numerically small, the Druze have significantly contributed to the history and cultural diversity of the Middle East.

